|
Some informations about Greece
Greece, also known as Hellas and officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in southeastern Europe, forming the southern tip of the Balkan Peninsula and is made up of a series of mountains that run into the sea, extending into scattered islands through the Aegean Sea in the east. Greece has the tenth longest coastline in the world at 14.880 km in length, featuring a vast number of islands (approximately 1.400, of which 227 are inhabited). Eighty percent of Greece consists of mountains, of which Mount Olympus is the highest at 2.917 m.
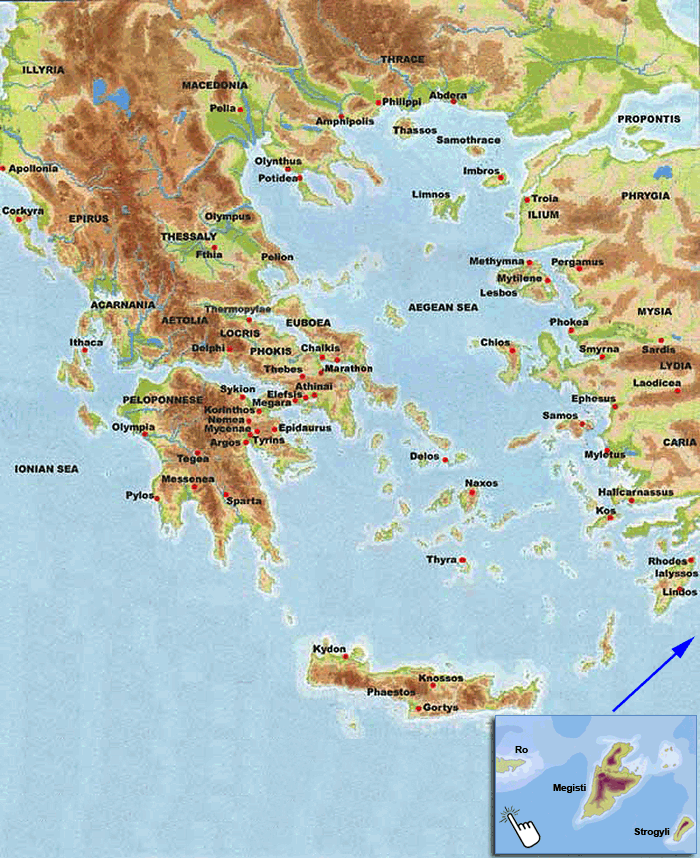
Geophysical Map of Greece with the ancient names
|
Modern-day Greece is a nation of many islands, but in ancient times, Greece was a loose confederation of city-states that usually only came together as a whole to defend themselves from invaders. With easy access to the Mediterranean Sea to the south and the Aegean Sea to the north and northeast, Athens was among the most powerful of the city states.
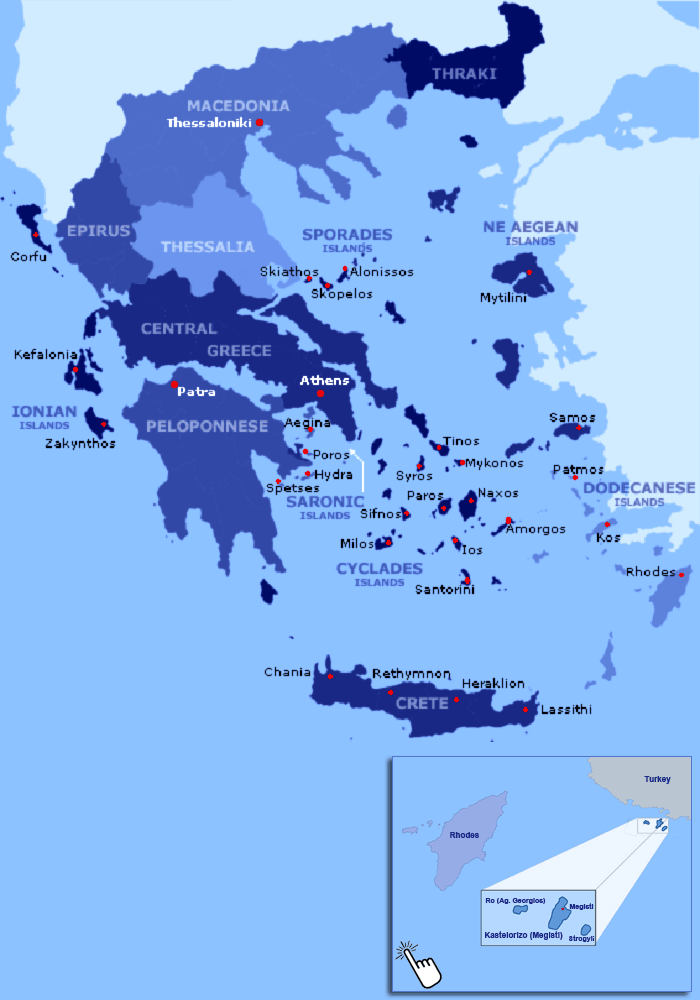
Political Map of Greece
|
More recently, Athens has again become the center of the world's attention as the Olympic Games returned to their modern birthplace in August 2004. The ancient Games began in 776 BC in the city of Olympia on the northwest side of Peloponnesus. About 2.700 years later, in 1896, the Olympics were reborn in Athens. The 2004 Olympics mark the 28th modern Olympiad. Greece was the first area in Europe where advanced early civilizations emerged, beginning with the Cycladic civilization of the Aegean Sea, the Minoan civilization in Crete and then the Mycenaean civilization on the mainland. Later, city-states emerged across the Greek peninsula and spread to the shores of the Black Sea, South Italy and Asia Minor, reaching great levels of prosperity that resulted in an unprecedented cultural boom, that of classical Greece, expressed in architecture, drama, science and philosophy and nurtured in Athens under a democratic environment.
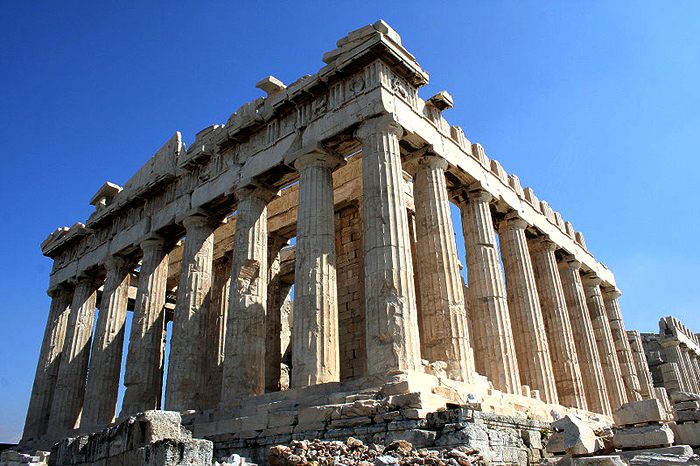

The Parthenon on the Acropolis of Athens
|
Modern Greece traces its roots to the civilization of ancient Greece, generally considered to be the cradle of Western civilization. As such, it is the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, the Olympic Games, Western literature and historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles and Western drama, including both tragedy and comedy. This legacy is partly reflected in the 17 UNESCO World Heritage Sites located in Greece. A developed country with a very high Human Development Index and standard of living, Greece has been a member of what is now the European Union since 1981 and its Economic and Monetary Union since 2001, NATO since 1952, and the European Space Agency since 2005. It is also a founding member of the United Nations, the OECD, and the Black Sea Economic Cooperation Organization. Athens is the capital. Other major cities include Thessaloniki, Piraeus, Patras, Heraklion and Larissa.
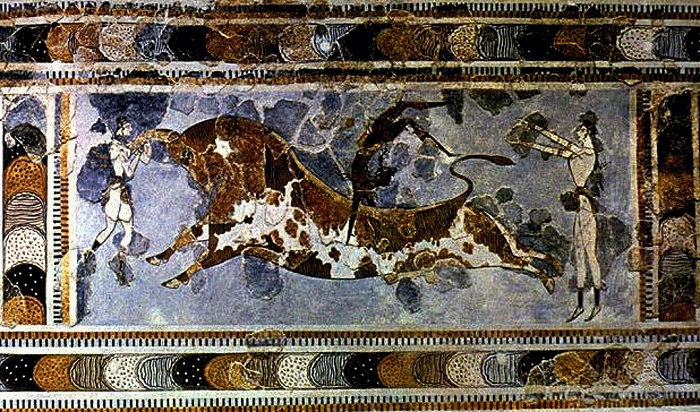
Bull-leaping (taurokathapsia) fresco from the Great Palace at Knossos, Crete
|
|
